There are many types of Vanish on the market, which can be divided into two categories: solvent type and non-solvent type.
But both actually contain organic solvents (usually styrene); what is the difference?
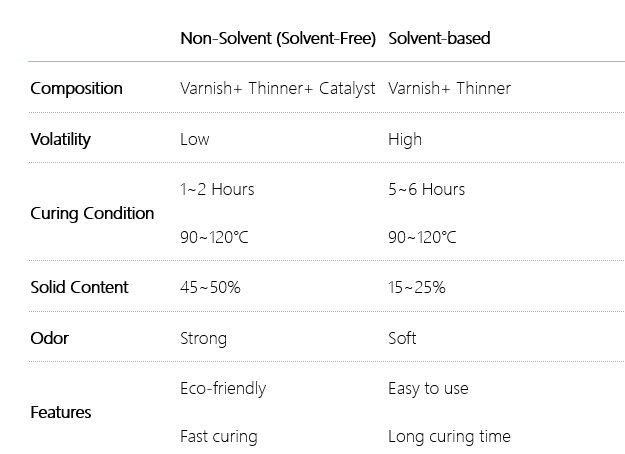
Ⅰ. Composition
The content of organic solvent in the main agent (Vanish) is different.
The non-solvent type of Vanish has high solid content and is more environmentally friendly (with less volatilization), and the organic solvent content is low, but additional hardeners are needed to bridge it; solvent type Vanish has low solid content and high organic solvent content, but it is used conveniently with no need to add hardener.
Solvent type: main agent (Vanish) + thinner
Non-solvent type: main agent (Vanish) + thinner + hardener
Japanese manufacturers (Hitachi Chemical, Kyocera, etc.) mostly use non-solvent types.
European and American manufacturers (Dolph, Elantas, etc.) mostly use solvent-based types.
Ⅱ. Baking time
The two have different baking time due to the difference in solid content. Generally speaking:
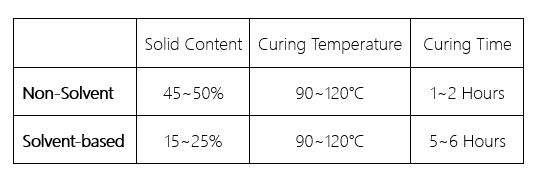
Shorter baking time means higher production efficiency and less energy consumption.
Ⅲ. Odor
Generally speaking, because of different formulations, the odor of non-solvent type is greater than that of solvent type Vanish.
However, the non-solvent type has low volatile content, and the odor does not cause harm to the human body.
Ⅳ. Summary
Here is a table to briefly explain the difference between the two for clear understanding of how to choose solvent and non-solvent products.